iPNHOT: A webserver for predicting hotspots at protein-nucleic acid interfaces
The iPNHOT Server is a web-based implementation of iPNHOT model — a machine learning approach for predicting binding hot spots on protein-nucleic acid interfaces. The server facilitates the automated analysis of a given chain of protein and the visualization of its hot spot predictions. For each residue within the interface, the iPNHOT Server characterizes the atom number, depth and protrusion index, solvent accessible surface area, electrostatic potential, and secondary structure. Then the model predicts if the residue is a hot spot or not. The user can visualize the residue by clicking the corresponding row of the table after the computational analysis is complete.
The iPNHOT model is built by Support Vector Machine using the 9 features selected by decision tree and SFS. For this work, hot spots are defined as mutations associated with a change in binding energy (∆∆G) greater than 2 kcal/mol.
The iPNHOT server requires a modern web browser with JavaScript and cookies enabled. To view the complex details, pop-ups must not be blocked.The following browsers have been throughly tested with iPNHOT:
- Mozilla Firefox, version 4 or above
- Chrome, version 5 or above
- Internet Explorer, versions 7, and 8 or above
The latest version of Firefox and Chrome is recommended for visualization.

Before the iPNHOT analysis can begin, a user must provide a PDB file that contains the structure of a protein-nucleic acid complex, a protein chain of the protein-NA interface for analysis. Files that do not contain a bound complex are unlikely to yield useful results. In addition, model structures containing many clashes may vastly overestimate the number of hot spots. Finally, iPNHOT is able to analyze proteins but not other types of molecules.
To analyze a protein chain of a protein-NA interface, enter the following information on the submission page and click the SUBMIT button.
• PDB File Upload — Link to PDB file of a protein complex (e.g. "1aay.pdb")
• Chain id — A chain of a protein-protein interface for analysis (e.g. "A")
Upon submission, the task will wait for processing. After processing begins, a typical iPNHOT analysis finishes within a minute. When the task is complete, a result is displayed to the user with their iPNHOT hot spot predictions or an error message. If the job finishes successfully, the status field will contain a table of results. Jobs that end in error are described by the following warnings:
• Your PDB file could not be uploaded because: No file was uploaded.
• Please assign a chain ID of your PDF file.
Users can access an iPNHOT output by clicking the “Download” button. Most errors are caused by non-standard amino acids or ligands incorrectly labeled as ATOM records within the PDB coordinate file. If possible, the user should resolve the inconsistencies in the file and submit a new job. If subsequent jobs still end in error, users can contact xlzhu_mdl@hotmail.com for assistance.
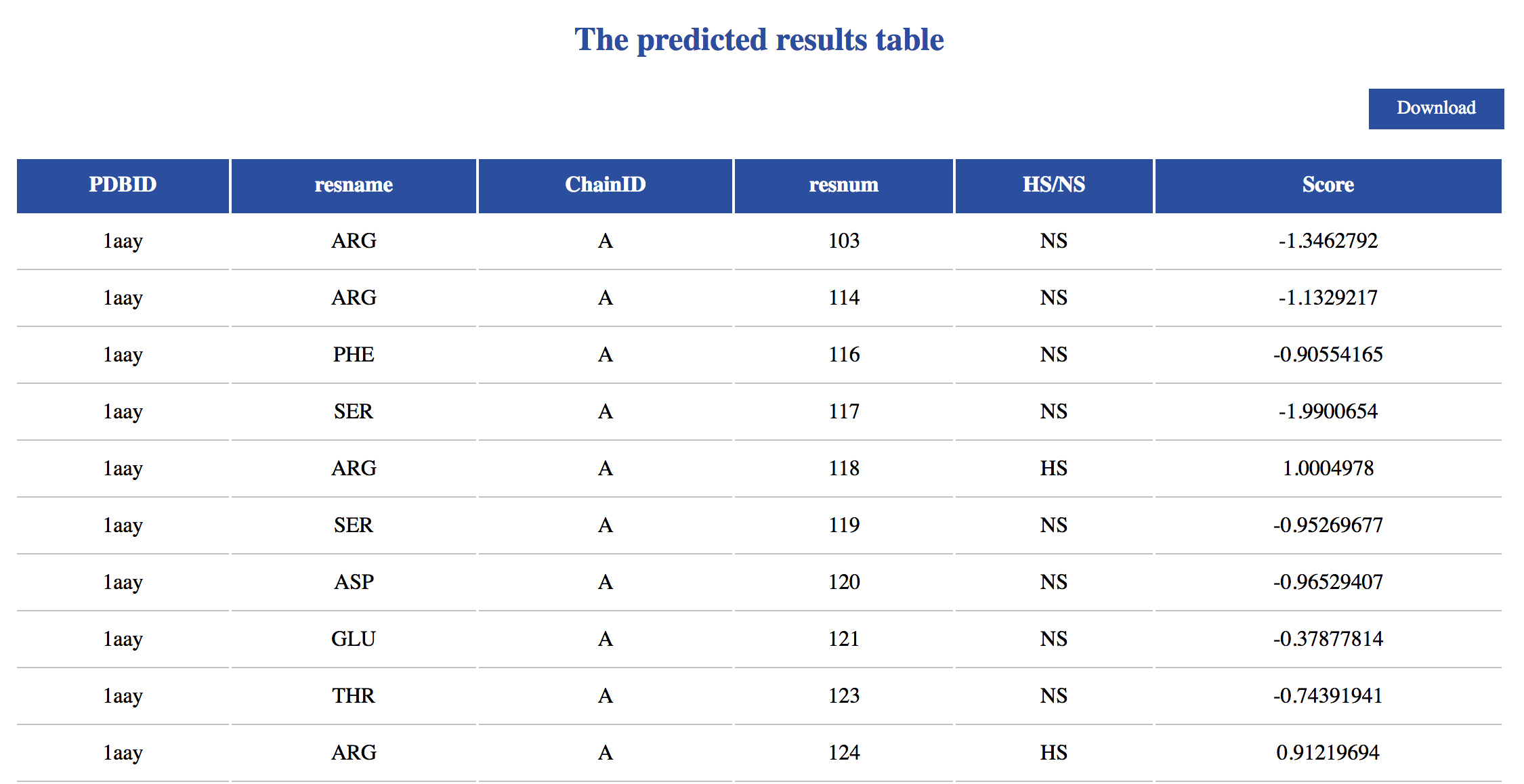
• PDBID — Protein identifier from PDB file.
• resname — Amino acid residue name.
• ChainID — Chain identifier chosen from PDB file.
• resnum — Residue number from PDB file.
• HS/NS — Hot spot(HS)/non-hot spot(NS) predicted as by iPNHOT.
• Probability — Probability of prediction by iPNHOT.
• Download — On the uperright, users can click download to downlaod all the results.
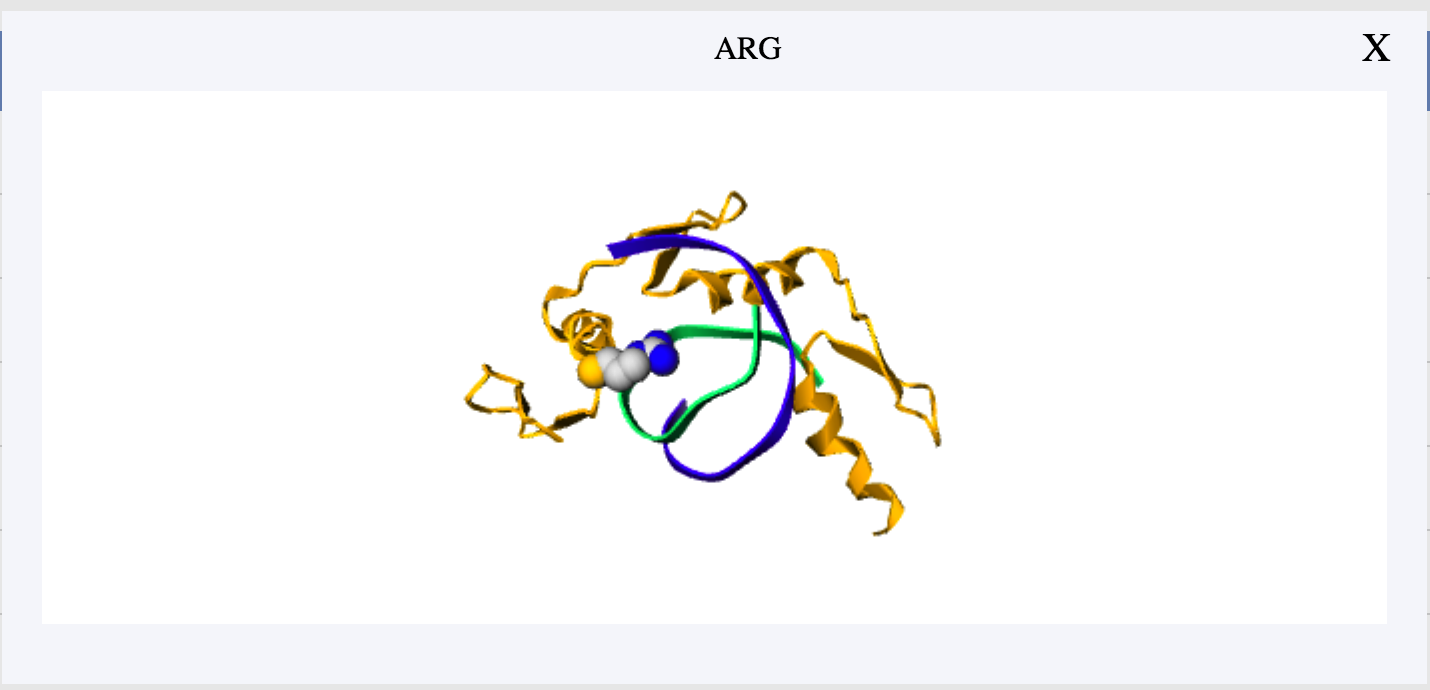
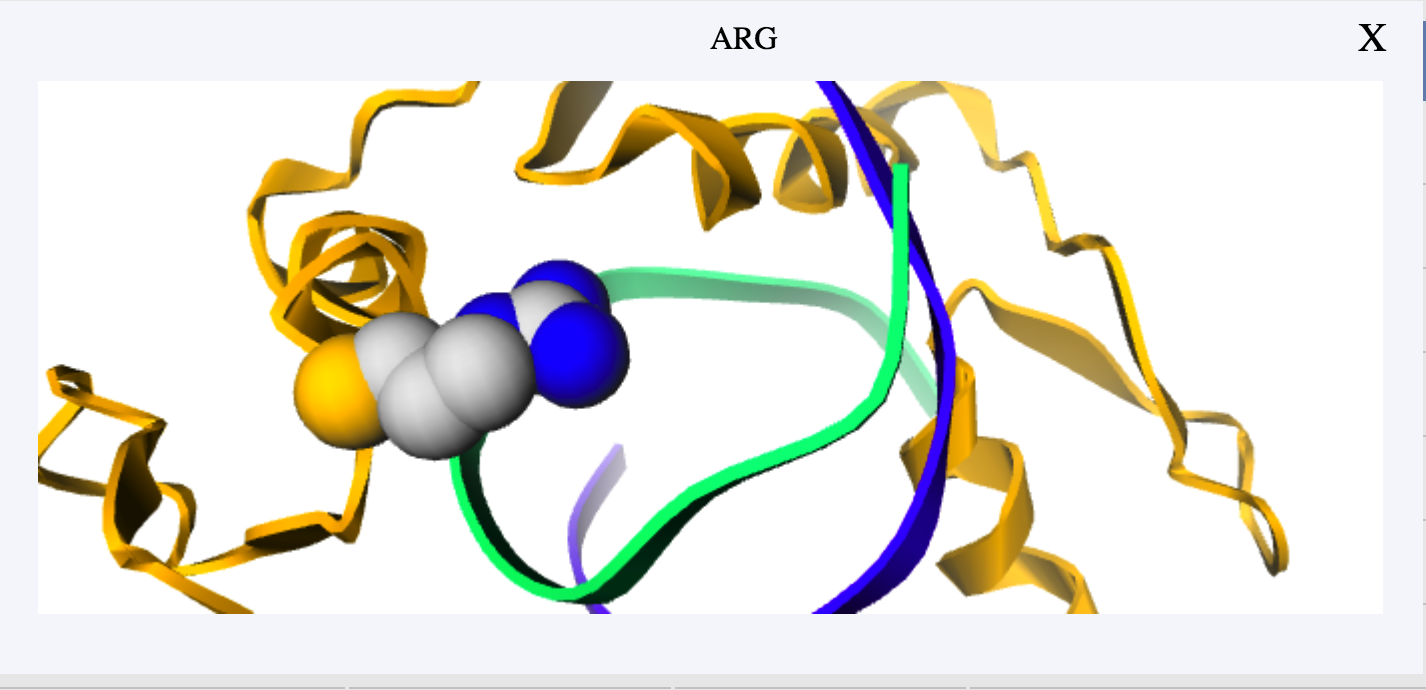
Users can directly click the corresponding row to view a residue in the table. Meanwhile, scaling and spin are available for further observation.

If you have any suggestion or problem about iPNHOT server , please send us email directly.